Parler
Parler Gab
Gab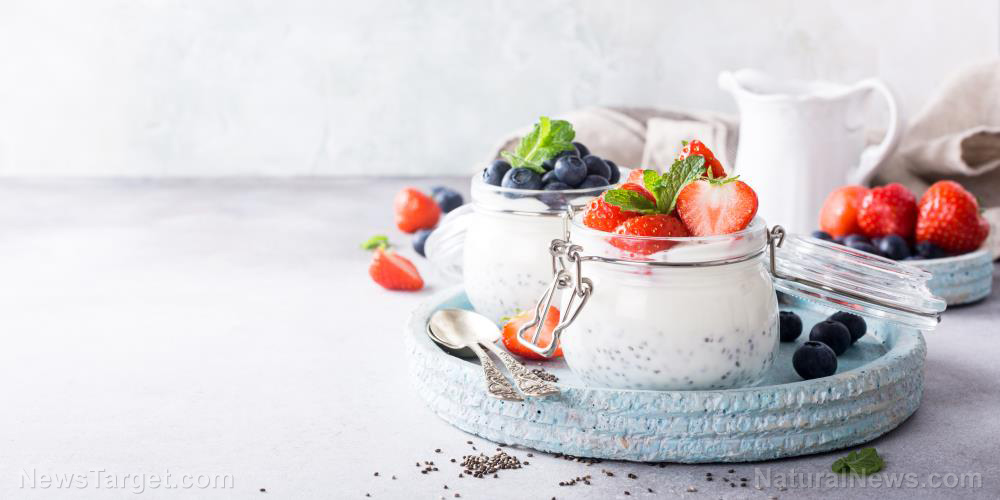
- Greek yogurt is a thick, protein-rich strained yogurt made by fermenting milk with live bacterial cultures. The straining process removes whey and lactose, making it denser and higher in protein than regular yogurt.
- It originated in the Middle East and Central Asia and was popularized by the ancient Greeks and Turks. It also gained global fame in the 2000s due to brands like Fage and Chobani.
- Greek yogurt is high in protein (15–20g per 6 oz), probiotics for gut health, and essential nutrients like vitamin B12, potassium and phosphorus. It is lower in sugar and carbs than regular yogurt, making it ideal for blood sugar management.
- It is generally healthy but may affect lactose-intolerant individuals. Plain, unsweetened versions are the best; flavored options often contain added sugars. Additionally, organic yogurt reduces exposure to pesticides, hormones and heavy metals.
- It is versatile and suits sweet and savory dishes. Greek yogurt can be used to make smoothies, dips (tzatziki), baking, marinades and desserts. Popular recipes include yogurt pancakes, chicken salad, banana bread and cheesecake.
Ancient origins and modern popularity
Greek yogurt, also known as "strained yogurt," is a thick, protein-rich dairy product made by fermenting milk with live bacterial cultures (such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus). The key difference between Greek yogurt and regular yogurt lies in the straining process: Greek yogurt is strained multiple times to remove whey, lactose and excess liquid, resulting in a denser, creamier texture with higher protein content. Yogurt has been consumed for thousands of years, with evidence suggesting it originated in the Middle East and Central Asia. The ancient Greeks and Turks were among the first to popularize strained yogurt, using it in both culinary and medicinal applications. Greek yogurt as we know it today gained global recognition in the early 2000s, thanks to brands like Fage and Chobani introducing it to Western markets. Its high protein content and versatility quickly made it a favorite among health-conscious consumers. (Related: Studies show that adding HONEY to YOGURT can help improve your gut health.)Nutritional benefits
Greek yogurt is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a wealth of essential nutrients in every serving. A typical six-ounce (170 grams, g) serving of plain, non-fat Greek yogurt provides:- 15–20 g of protein (nearly double that of regular yogurt)
- 10–20 percent of the Daily Value (DV) for protein
- Support for gut health and digestion through its abundance of probiotics
- Energy and nerve support through vitamin B12
- Blood pressure regulation through potassium
- Bone support through phosphorus
How to choose the best Greek yogurt
Greek yogurt is generally considered to be a highly nutritious addition to most diets, though there are a few factors to keep in mind. For individuals with lactose intolerance, Greek yogurt can still cause discomfort despite containing less lactose than regular yogurt. Full-fat Greek yogurt provides healthy fats but can be higher in calories, while low-fat versions are leaner but may contain added sugars. Flavored yogurts are typically high in sugar, making plain Greek yogurt a healthier choice. Overall, Greek yogurt is widely regarded as a superfood, especially when consumed in its simplest, least processed form. When choosing Greek yogurt, organic options may offer additional benefits. Conventional dairy products can contain traces of pesticides from feed, as well as synthetic hormones like rBGH, whereas organic Greek yogurt is produced without these additives. Dairy products are generally low in heavy metals, but contaminants like cadmium and lead can still be present in trace amounts depending on farming practices. Organic farming helps reduce exposure to these pollutants. Additionally, organic certification ensures cows are not treated with antibiotics, lowering the risk of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.Culinary uses and recipes
Greek yogurt's thick texture and mild tang make it a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes. Here are some common uses:Breakfast and smoothies
- Parfaits - Layered with granola, berries and honey
- Smoothie base - Adds creaminess and protein to fruit smoothies
Dips and sauces
- Tzatziki - A classic Greek dip with cucumber, garlic and dill
- Ranch or dill dip - A healthier alternative to sour cream
Baking and desserts
- Yogurt cake - Adds moisture to baked goods
- Frozen yogurt - A lighter alternative to ice cream
Savory dishes and marinades
- Marinades - Tenderizes meat while adding flavor
- Creamy soups and dressings - Replaces heavy cream in recipes
- Greek yogurt pancakes – Fluffy, protein-packed pancakes
- Greek yogurt chicken salad – A lighter take on classic chicken salad
- Greek yogurt banana bread – Moist and nutritious
- Greek yogurt cheesecake – A low-calorie dessert option
- Greek yogurt pasta sauce – A creamy, protein-rich Alfredo alternative
More related stories:
Yogurt and probiotic-rich foods can help lower blood pressure.
From gut health to antibiotics: How do bacteria affect your life? Probiotics and yogurt exhibit potential anti-schistosomal, hepatoprotective properties. Sources include: Brighteon.AI NaturalNews.com Brighteon.comHow Lingzhi mushrooms (Reishi) combats aging, disease and cancer
By News Editors // Share
A comprehensive guide to DANDELIONS, an ancient herbal medicine and superfood
By Ava Grace // Share
Spirulina: The protein-packed algae taking over wellness trends
By Laura Harris // Share
The power of activated charcoal: An ancient remedy proven to improve kidney function
By News Editors // Share
Why essential oils are must-have barter items when SHTF
By HRS Editors // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share