Parler
Parler Gab
Gab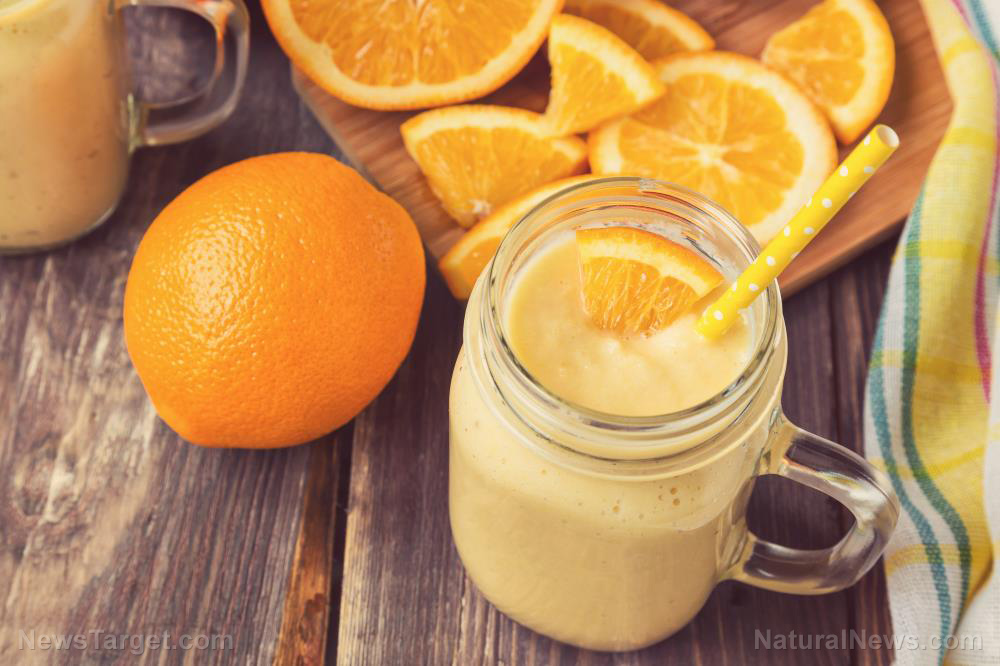
- Oranges (Citrus x sinensis) are a beloved fruit, celebrated for their vibrant color, refreshing taste and impressive nutritional profile.
- Sweet oranges are spherical with a bright orange hue, textured skin and juicy, segmented flesh.
- Originating in Southeast Asia around 2500 BCE, they spread globally via trade routes, reaching Europe by the 15th century and the Americas through Spanish explorers. Today, Brazil, the U.S. and China are the top producers of oranges.
- Oranges are rich in phytonutrients, including carotenoids, dietary fiber, flavonoids, potassium and vitamin C. These compounds support immune function, heart health, skin health, digestion and vision while reducing inflammation and cancer risk.
- Oranges are a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes. Popular recipes include orange-glazed salmon, orange chicken stir-fry, citrus salad with arugula and feta, and orange and almond cake.
The orange: A closer look
Oranges are instantly recognizable by their bright orange hue, though some varieties, like the blood orange, may have a deep red or maroon interior. The fruit is typically spherical with a slightly flattened shape, and its skin is textured with tiny pores that release aromatic oils when pressed. The flesh is segmented, juicy and encased in a thin, white pith that is rich in bioflavonoids. The taste of an orange is a harmonious blend of sweetness and tanginess, making it a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes.Historical and cultural significance
Sweet orange is believed to have originated in Southeast Asia, specifically in the region encompassing southern China and northeastern India. Historical records suggest that oranges were cultivated in China as early as 2500 BCE. From there, they spread to the Middle East and Mediterranean regions through trade routes. By the 15th century, oranges had reached Europe, where they became a luxury item among the elite. Spanish explorers later introduced oranges to the Americas, where they flourished in the warm climates of Florida and California. Today, Brazil, the United States and China are among the top producers of oranges globally.Nutritional composition and phytonutrients
Oranges are a treasure trove of phytonutrients, which are bioactive compounds that contribute to their health benefits. These compounds include:- Carotenoids – Carotenoids like beta-carotene and lutein help support eye health and immune function.
- Dietary fiber – Fiber aids in digestion and supports gut health.
- Flavonoids – Flavonoids like hesperidin and naringenin are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Potassium – Potassium is essential for heart health and maintaining electrolyte balance.
- Vitamin C – A potent antioxidant that boosts immunity and promotes skin health.
Health benefits and potential therapeutic uses
Oranges are more than just a tasty snack; they are a functional food that can help prevent and even reverse certain health conditions. (Related: Hidden gem of the tropics: Nance fruit’s incredible health benefits.) Below are some of the key benefits of eating oranges, according to science:- Boosts immune function – The high vitamin C content of oranges can strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections.
- Supports heart health – The flavonoids and potassium in oranges can help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Improves skin health – Vitamin C promotes collagen production, which keeps the skin firm and reduces signs of aging.
- Aids digestion – The dietary fiber in oranges can support healthy digestion and prevents constipation.
- Reduces inflammation – The anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids can help alleviate symptoms of chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
- Protects vision – Carotenoids like beta-carotene and lutein are essential for maintaining eye health and preventing age-related macular degeneration.
- Lowers cancer risk – The antioxidants in oranges can neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and the risk of certain cancers.
Culinary applications and recipe ideas
Oranges are incredibly versatile in the kitchen, adding a burst of flavor and nutrition to a wide range of dishes. Here are some recipe ideas that showcase the fruit’s versatility:- Orange glazed salmon – A savory dish where orange juice and zest create a tangy glaze for grilled or baked salmon.
- Orange chicken stir-fry – A quick and healthy meal featuring tender chicken, crispy vegetables and a zesty orange sauce.
- Citrus salad with arugula and feta – A refreshing salad combining orange segments, peppery arugula and creamy feta cheese.
- Orange and almond cake – A moist, gluten-free dessert that highlights the natural sweetness of oranges.
- Orange smoothie bowl – A nutrient-packed breakfast option blending oranges, bananas and yogurt, topped with granola and fresh berries.
More related stories:
Devil’s claw: A medicinal herb that can boost heart health. Organic coffee gardening tips for spring enthusiasts. Grapefruit found to help reduce high blood pressure. Sources include: Brighteon.AI NaturalNews.com Brighteon.comRethinking autism: How maternal health during pregnancy influences a child’s autism risk
By Olivia Cook // Share
Summer savory: The sun-loving herb that supports health and wellness
By Ava Grace // Share
What is the liver powerhouse silymarin?
By News Editors // Share
States race to ban toxic food dyes as RFK Jr. pushes industry for reform
By Cassie B. // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share