Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
Ginsenosides kill cancer cells
Researchers in a study from the journal Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine reviewed and discussed all available literature to facilitate further research on ginsenosides and their role in the treatment of different types of cancer.Brain cancer
Researchers in a study from the Journal of Ginseng Research reported that in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) – the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults and a challenging disease to be treated – ginsenoside F2 induced glioma stem cells, including CD133 cells (one of the most well-characterized biomarkers used for the isolation of cancer stem cells), to commit apoptosis and inhibit new blood cells from forming.Breast cancer
One study from September 2023 published in Frontiers in Pharmacology updated the therapeutic role of ginsenosides in breast cancer treatment and summarized its mechanisms of action, which include inducing apoptosis, autophagy, inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis, and regulating miRNA and lncRNA. Ginsenoside clears out damaged or abnormal cells – preempting their potentially damaging impact; regulates cancer cell cycle growth and proliferation; induces self-degradation; inhibits cancer cell spread from the primary tumor in the breast to other parts of the body; regulates EMT or the process by which breast epithelial cells transform into mesenchymal stem cells, which are more motile and invasive and regulates miRNAs, which can act as either tumor suppressors or oncogenes that can transform a normal cell into a tumor cell.Gastric cancer
In another study from Frontiers in Pharmacology, this time from October 2022, researchers referred to ginsenosides as "allies of gastrointestinal (GI) tumor immunotherapy." The study reported that ginsenosides and related preparations have been clinically used in cancer treatment for a long time and have played important roles in the improvement of post-operative fatigue after cancer, reversing drug resistance and enhancing the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Researchers suggested that ginsenosides could potentially complement the first-line anti-GI tumor drugs – improving treatment effects and patient survival times and quality of life.Liver cancer
According to a study from the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma development by targeting the gut-liver axis. Results of the study suggested that ginsenoside Rk3 application inhibited liver injury, fibrosis, or the overgrowth, hardening and/or scarring of various tissues) and cirrhosis – a condition in which the liver is scarred and permanently damaged.Lung cancer
In a study published in Food & Function, in in vivo and in vitro lung cancer models, ginsenosides Rg3, Rh2, and CK were reported to have strong anti-lung cancer effects. Researchers also observed remarkable protective action from ginsenoside Rb1 in the models of pneumonia and acute lung injury by alleviating inflammation and oxidative stress and inducing apoptosis. Moreover, researchers reported on the health-promoting effects of ginsenosides in the improvement of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma and pulmonary fibrosis (PF). The study suggested ginsenosides as a potential natural medicine to protect the lungs from lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease.Adding ginseng to your diet
Ginseng root can be eaten raw or you can lightly steam it to soften the herb. (Related: Ginseng – Benefits of the popular Chinese root.) Others add hot water to freshly sliced ginseng and let it steep for several minutes to make tea. Fresh or powdered ginseng can be added to various recipes like soups and stir-fried dishes, too. Additionally, the extract can be found in capsule, oil, tablet and oil forms. How much you should take depends on the condition you want to improve. Overall, daily doses of one to two grams of raw ginseng root or 200 to 400 milligrams of extract are suggested. It’s best to start with lower doses and increase over time. It is highly recommended that you talk to your doctor before supplementing with ginseng. Look for a standard ginseng extract supplement that contains two to three percent total ginsenosides and consume it before meals to increase absorption and get ginseng’s full health benefits. Superfoods.news has more about the wonderful health benefits of ginseng. Watch the following video about ginseng's adaptogenic benefits. This video is from the Holistic Herbalist channel on Brighteon.com.More related stories:
Seven health benefits of ginseng. The superior health benefits of ginseng. Ginseng – Combat the effects of radiation. Sources include: NaturalHealth365.com PubMed.NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov FrontiersIn.org 1 Hindawi.com KoreaScience.or.kr FrontiersIn.org 2 FrontiersIn.org 3 Pubs.ACS.org Pubs.RSC.org Brighteon.comSkin age reversed 13 years in just 9 months by doing this
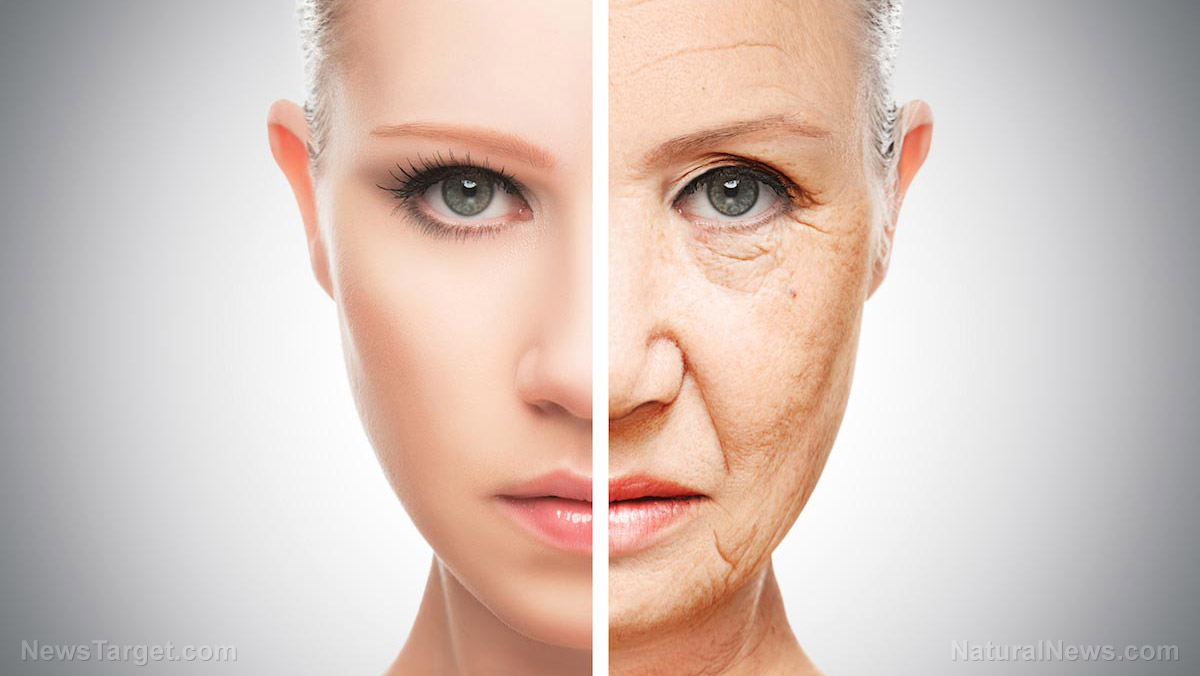
By News Editors // Share
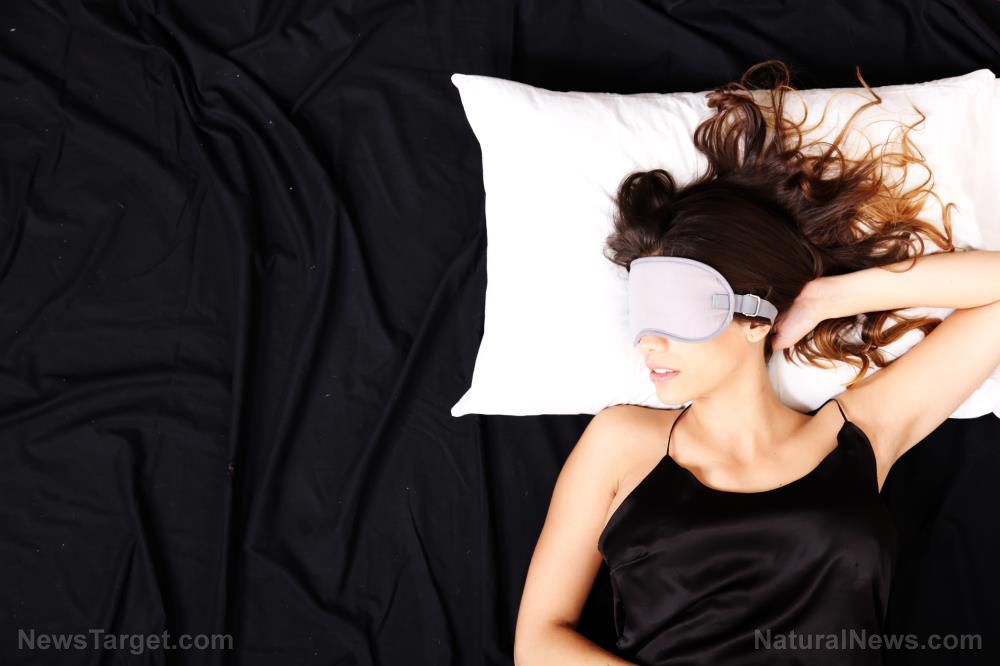
Study finds INSUFFICIENT SLEEP negatively impacts cardiovascular health
By Olivia Cook // Share
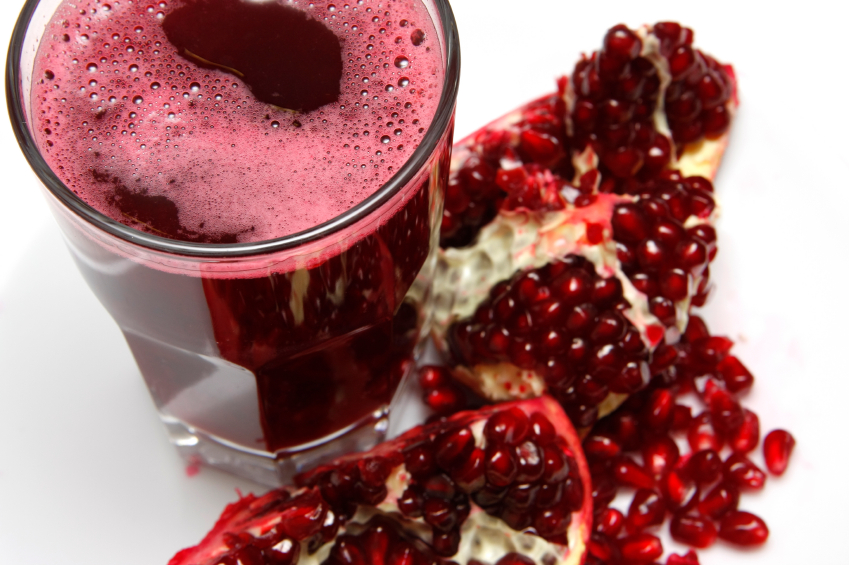
Why pomegranate juice is ‘roto-rooter’ for the arteries
By News Editors // Share
Study shows antioxidants in grapes can boost eye health
By Zoey Sky // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
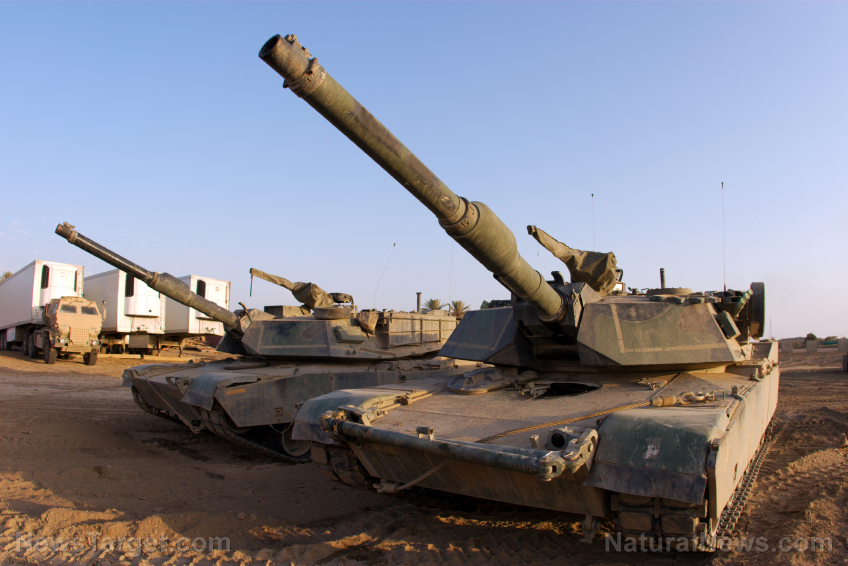
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share