Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
Countries with higher vaccination rates have higher mortality rates as well
In relation to the new study, Miller and Goldman conducted an earlier study in 2011 discussing the complex interplay between vaccination policies, public health conditions and socioeconomic well-being. According to the study, the U.S. boasts the most extensive childhood immunization schedule worldwide, with 26 vaccine doses recommended for infants under one year of age. The 2011 study revealed that 33 other countries have lower IMRs despite administering fewer vaccine doses. The researchers uncovered a correlation coefficient (r) of 0.70 (p < 0.0001) between IMRs and the number of vaccine doses regularly administered to infants through a meticulous analysis of the immunization schedules and IMRs of 34 nations. (Related: As vaccination rates go up, so does infant mortality - could injecting newborns with toxic chemicals be behind SIDS?) In statistical terms, an r-value exceeding zero indicates a positive correlation, while an r-value between 0.6 and 0.79 signifies a "strong" positive correlation. This implies that vaccines demonstrate a positive relationship with IMRs. Overall, both studies highlighted the fact that countries with extensive childhood vaccination programs tend to experience higher IMRs. Learn more about how childhood vaccination requirements are part of a covert genocide agenda at Vaccines.news. Watch the video below about data showing that COVID vaccines are actually killing children. This video is from the High Hopes channel on Brighteon.com.More related stories:
HOLOCAUST OF THE UNBORN: Babies are DYING because their mothers got “vaccinated” for covid.
COVID vaccines can damage innate immune systems of children, epidemiologist warns. CDC, FDA prepare mass distribution of a Merck/Sanofi six-in-one vaccine for kids, turning blind eye to safety signals. Sources include: ChildrensHealthDefense.org 1 Cureus.com ChildrensHealthDefense.org 2 Brighteon.comRetiring lieutenant exposes ‘spineless puppet’ chief who demoralized Seattle Police Department
By Belle Carter // Share
Chinese military says it just achieved “huge breakthrough” in laser weapon technology
By Ethan Huff // Share
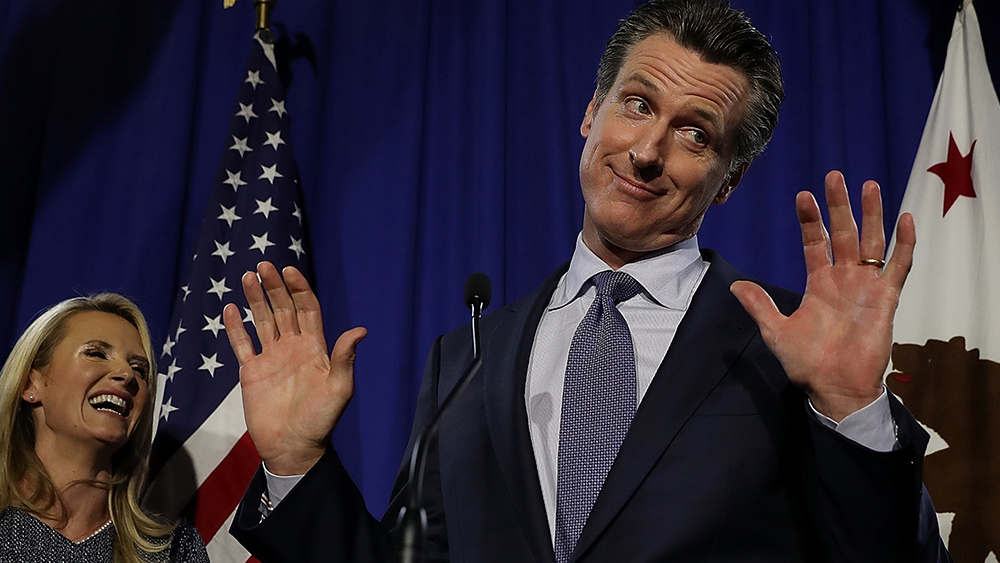
Gov. Gavin Newsom used taxpayer money to fund Chinese-backed biolab operations in California
By Laura Harris // Share
Young protesters use traffic cones to paralyze self-driving cars in San Francisco
By Laura Harris // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share