Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
- AgiBot successfully deployed Real-World Reinforcement Learning (RW-RL) in an active manufacturing line with Longcheer Technology. This marks the first industrial application of reinforcement learning in robotics, bridging AI research with real-world production.
- Traditional robots rely on rigid programming, requiring costly reconfiguration and custom fixtures. AgiBot's RW-RL system enables robots to learn and adapt on the factory floor, acquiring new skills in minutes instead of weeks while maintaining industrial-grade stability.
- Unlike lab-based RL, AgiBot's system was tested in near-production conditions, proving its industrial readiness. Robots demonstrated resilience against disruptions (temperature shifts, vibrations, misalignment) while maintaining precision assembly. When production models changed, robots retrained in minutes without manual reprogramming.
- AgiBot plans to expand RW-RL into consumer electronics and automotive manufacturing, focusing on plug-and-play robotic solutions. Their LinkCraft platform (converting human motion into robot actions) and G2 robot (powered by NVIDIA's Jetson Thor T5000) enable real-time AI processing. If scalable, this could usher in the adaptive factory era, where robots continuously learn and optimize without halting operations.
Key advantages of RW-RL
AgiBot highlights three core benefits of its reinforcement learning system:- Rapid Deployment – Training time slashed from weeks to minutes.
- High Adaptability – Robots autonomously compensate for variations like part misalignment while maintaining 100 percent task completion.
- Flexible Reconfiguration – Production line changes require minimal hardware adjustments, eliminating costly downtime.
The future of adaptive factories
AgiBot and Longcheer plan to expand RW-RL into consumer electronics and automotive manufacturing, focusing on modular, plug-and-play robotic solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing systems. The company's LinkCraft platform—which converts human motion videos into robot actions—complements this advancement, reducing programming barriers. Meanwhile, AgiBot's G2 robot, powered by NVIDIA's Jetson Thor T5000, suggests that real-time AI processing is enabling this leap forward. While Google's Intrinsic and NVIDIA's Isaac Lab have pioneered reinforcement learning frameworks, AgiBot appears to be the first to deploy RL in live production. If scalable, this could herald the adaptive factory era, where robots continuously learn, optimize and evolve—without halting operations. As factories face increasing demands for customization and rapid model changes, AgiBot's breakthrough may finally make self-learning robotics a commercial reality. Watch the video below about Chinese startup AgiBot beginning mass production of general-purpose humanoid robots. This video is from the SecureLife channel on Brighteon.com. Sources include: TheRobotReport.com BrightU.ai PRNewswire.com Ubergizmo.com Brighteon.comAn ominous warning from the epicenter of AI
By Willow Tohi // Share
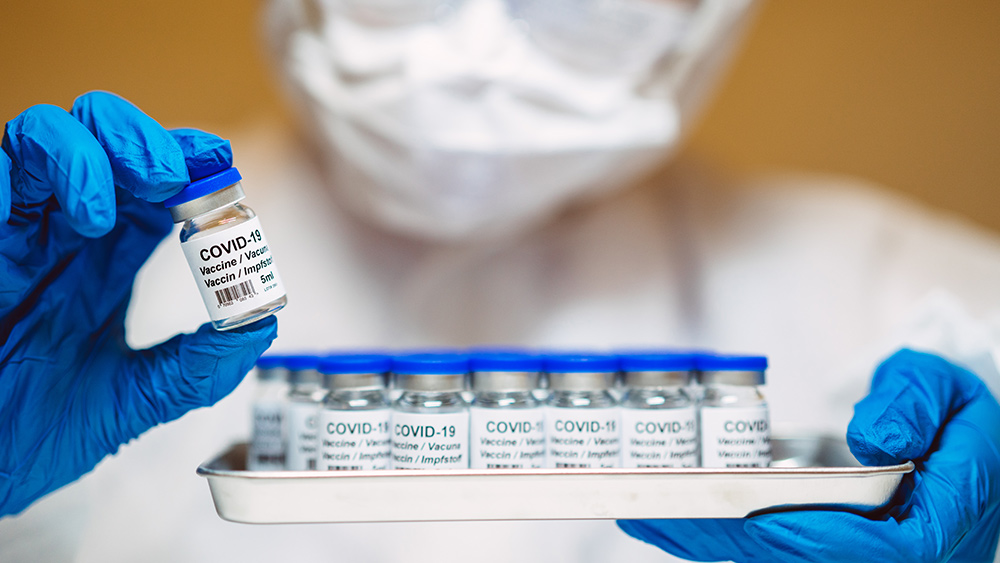
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share